The aim of this mission is to demonstrate the acceleration measurement capabilities of a quantum sensor in flight, in a dedicated satellite. The idea is to pave the way for the exploitation of quantum accelerometry technologies for space geodesy missions in the future.
Such missions are expected to provide more accurate determinations of the Earth’s gravitational field, leading to advances in Earth observation : ice melt, rainfall and drought, magma movements and tectonic plates...
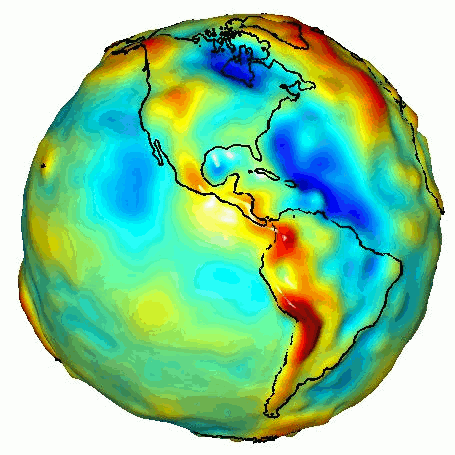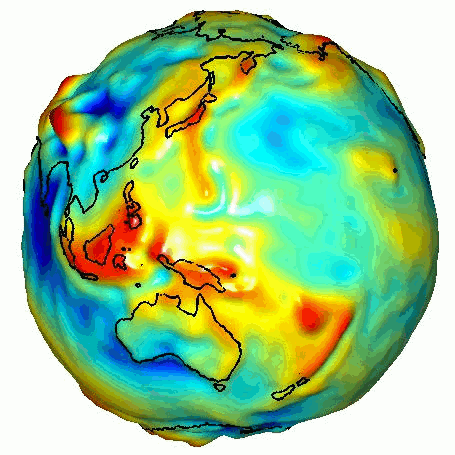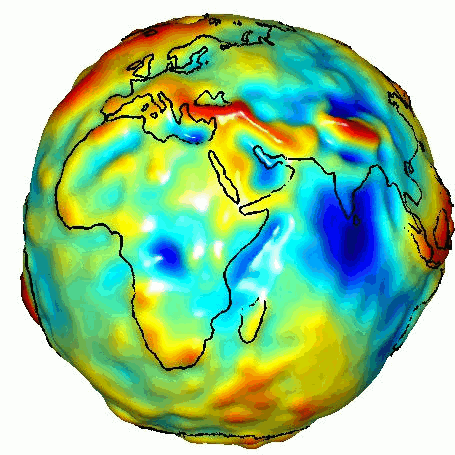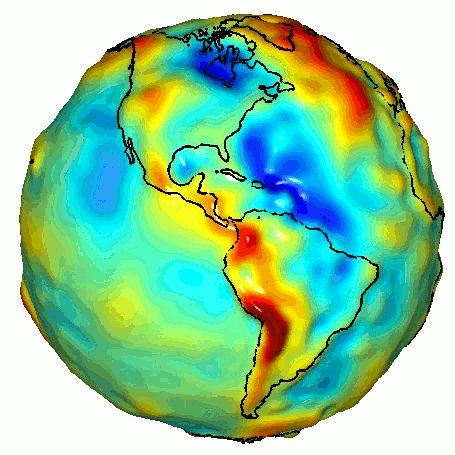
This ambition is supported by the European Commission, via project funding under the "Horizon Europe" program and its Quantum Plan, and shared by the French and German space agencies, CNES and DLR, which coordinate the European effort.
France will be heavily involved in the CARIOQA
mission.
with strong contributions :
- both scientific, with teams from the SYRTE laboratory at Observatoire de Paris - PSL, LP2N and ONERA ;
- and industrial contributions from Airbus Defence and Space SAS and eXail.
Since December 2022, these same players have been actively involved, along with other partners, particularly from Germany, Italy, Denmark and Greece, in the Horizon Europe project CARIOQA-PMP, which aims to build and ground test a prototype quantum accelerometer for space, as well as preparing future missions likely to carry this type of sensor.
