Comets are celestial bodies comprising a mixture of dust and ices, which they periodically shed as they swing towards their closest point to the Sun along their highly eccentric orbits.

As sunlight heats the frozen nucleus of a comet, the ice in it – mainly water but also other ‘volatiles’ such as carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide – turns directly into a gas.
This gas flows away from the comet, carrying dust particles along. Together, gas and dust build up the bright halo and tails that are characteristic of comets.
Rosetta arrived at Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko in August 2014 and has been studying it up close for over a year. On 13 August 2015, the comet reached the closest point to the Sun along its 6.5-year orbit, and is now moving back towards the outer Solar System.
A key feature that Rosetta’s scientists are investigating is the way in which activity on the comet and the associated outgassing are driven, by monitoring the increasing activity on and around the comet since Rosetta’s arrival.
Scientists using Rosetta’s Visible, InfraRed and Thermal Imaging Spectrometer, VIRTIS, have identified a region on the comet’s surface where water ice appears and disappears in sync with its rotation period. Their findings are published today in the journal Nature.
“We found a mechanism that replenishes the surface of the comet with fresh ice at every rotation : this keeps the comet ‘alive’,” says Maria Cristina De Sanctis from INAF-IAPS in Rome, Italy, lead author of the study.
The team studied a set of data taken in September 2014, concentrating on a one square km region on the comet’s neck. At the time, the comet was about 500 million km from the Sun and the neck was one of the most active areas.
As the comet rotates, taking just over 12 hours to complete a full revolution, the various regions undergo different illumination.
“We saw the tell-tale signature of water ice in the spectra of the study region but only when certain portions were cast in shadow,” says Maria Cristina.
“Conversely, when the Sun was shining on these regions, the ice was gone. This indicates a cyclical behaviour of water ice during each comet rotation.”
The data suggest that water ice on and a few centimetres below the surface ‘sublimates’ when illuminated by sunlight, turning it into gas that then flows away from the comet. Then, as the comet rotates and the same region falls into darkness, the surface rapidly cools again.
However, the underlying layers remain warm owing to the sunlight they received in the previous hours, and, as a result, subsurface water ice keeps sublimating and finding its way to the surface through the comet’s porous interior.
But as soon as this ‘underground’ water vapour reaches the cold surface, it freezes again, blanketing that patch of comet surface with a thin layer of fresh ice.
Eventually, as the Sun rises again over on this part of the surface on the next comet day, the molecules in the newly formed ice layer are the first to sublimate and flow away from the comet, restarting the cycle.
“We suspected such a water ice cycle might be at play at comets, on the basis of theoretical models and previous observations of other comets but now, thanks to Rosetta’s extensive monitoring at 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, we finally have observational proof,” says Fabrizio Capaccioni, VIRTIS principal investigator at INAF-IAPS in Rome, Italy.
From these data, it is possible to estimate the relative abundance of water ice with respect to other material. Down to a few cm deep over the region of the portion of the comet nucleus that was surveyed, water ice accounts for 10–15% of the material and appears to be well-mixed with the other constituents.
The scientists also calculated how much water vapour was being emitted by the patch that they analysed with VIRTIS, and showed that this accounted for about 3% of the total amount of water vapour coming out from the whole comet at the same time, as measured by Rosetta’s MIRO microwave sensor.
“It is possible that many patches across the surface were undergoing the same diurnal cycle, thus providing additional contributions to the overall outgassing of the comet,” adds Dr Capaccioni.
The scientists are now busy analysing VIRTIS data collected in the following months, as the comet’s activity increased around the closest approach to the Sun.
“These initial results give us a glimpse of what is happening underneath the surface, in the comet’s interior,” concludes Matt Taylor, ESA Rosetta Project Scientist.
“Rosetta is capable of tracking changes on the comet over short as well as longer time scales, and we are looking forward to combining all of this information to understand the evolution of this and other comets.”
Notes for Editors
“The diurnal cycle of water ice on cometary nuclei,” by Maria Cristina De Sanctis et al. is published in the 24 September 2015 issue of Nature.
The results are based on images and spectra taken at visible and infrared wavelengths of light on 12–14 September 2014 with VIRTIS.
These results will be presented next week at the European Planetary Science Congress, taking place from 27 September to 2 October 2015 in Nantes, France.
About Rosetta
Rosetta is an ESA mission with contributions from its Member States and NASA. Rosetta’s Philae lander is contributed by a consortium led by DLR, MPS, CNES and ASI.

Maps of water ice abundance (left) and surface temperature (right) focusing on the Hapi ‘neck’ region of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. These maps are based on images and spectra collected with Rosetta’s Visible, InfraRed and Thermal Imaging Spectrometer, VIRTIS on 12 (top), 13 (middle) and 14 September (bottom) 2014.
The ice abundance map is based on images taken with VIRTIS in the optical band at 0.7 micron and VIRTIS infrared spectra, combined with models of the surface and near-surface material. The infrared spectra taken in low illumination conditions show a strong dip at wavelengths between 2.7 and 3.6 micron, showing the characteristic shape of an absorption feature caused by water ice on the surface. In the water ice abundance maps, white indicates higher abundance of ice on the surface (over 5%) while blue hues indicate lower abundances : the darker blue, the lower abundance of ice, down to 0%.
The surface temperature maps are based on VIRTIS spectra at wavelengths above 4.5 micron. White and brighter hues indicate higher temperatures, with the highest temperature shown reaching –63ºC ; darker and redder hues indicate lower temperatures, with the darkest hues indicating surface temperatures around –133ºC.
The 12 and 13 September maps are separated by about one comet rotation, while the 13 and 14 September maps are separated by three rotations. Due to the complex topography of the comet, the illumination conditions were different in each of the three occasions.
By comparing the two series of maps, the scientists have found that, especially on the left side of each frame, water ice is more abundant on colder patches (white areas in the water ice abundance maps, corresponding to darker areas in the surface temperature maps), while it is less abundant or absent on warmer patches (dark blue areas in the water ice abundance maps, corresponding to brighter areas in the surface temperature maps). In addition, water ice was only detected on patches of the surface when they were cast in shadow.
This indicates a cyclical behaviour of water ice during each comet rotation.
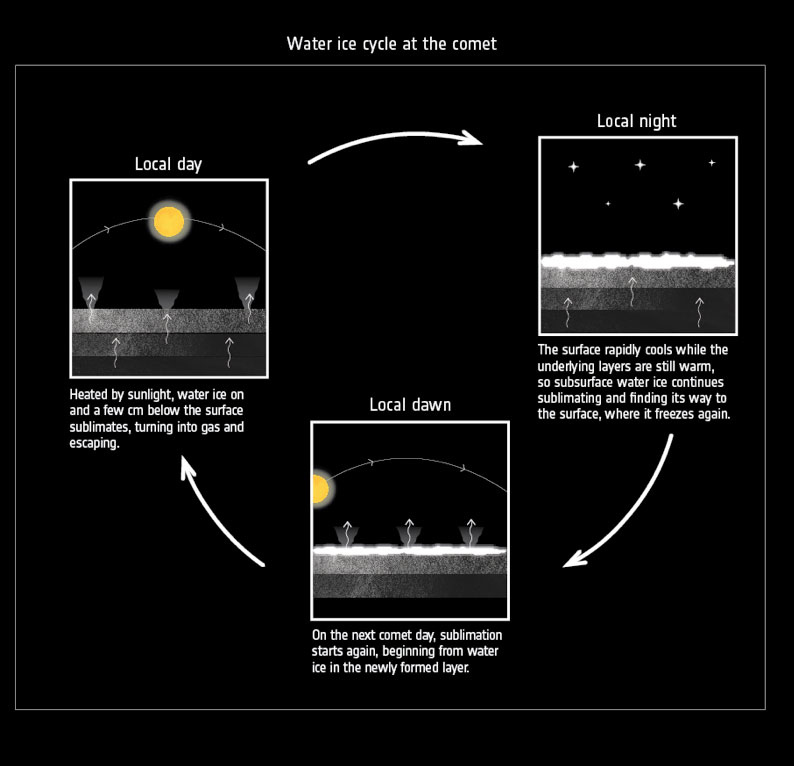
The daily water ice cycle of Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. During the local day, water ice on and a few centimetres below the surface sublimates and escapes ; during the local night, the surface rapidly cools while the underlying layers are still warm, so subsurface water ice continues sublimating and finding its way to the surface, where it freezes again. On the next comet day, sublimation starts again, beginning from water ice in the newly formed surface layer.
